Level 2 Market Depth Explained
Learn about detailed market depth data
Level 2 Market Depth Explained
Master the art of reading order books for superior trading decisions
What is Level 2 Market Depth?
Level 2 market depth, also known as the order book or market depth, reveals the complete picture of pending orders in the futures market. While Level 1 market data shows you where the market is now, Level 2 shows you where it might go next by displaying what's happening below the surface.
Level 2 data displays multiple price levels beyond the best bid and ask, showing you the exact number of contracts waiting to buy or sell at each price level. This granular view into market structure gives futures traders a significant edge in understanding supply and demand dynamics before they show up in price action.
Think of Level 1 data as seeing only the tip of an iceberg, while Level 2 reveals the entire underwater structure that could impact price movement.
How Does Level 2 Market Depth Work?
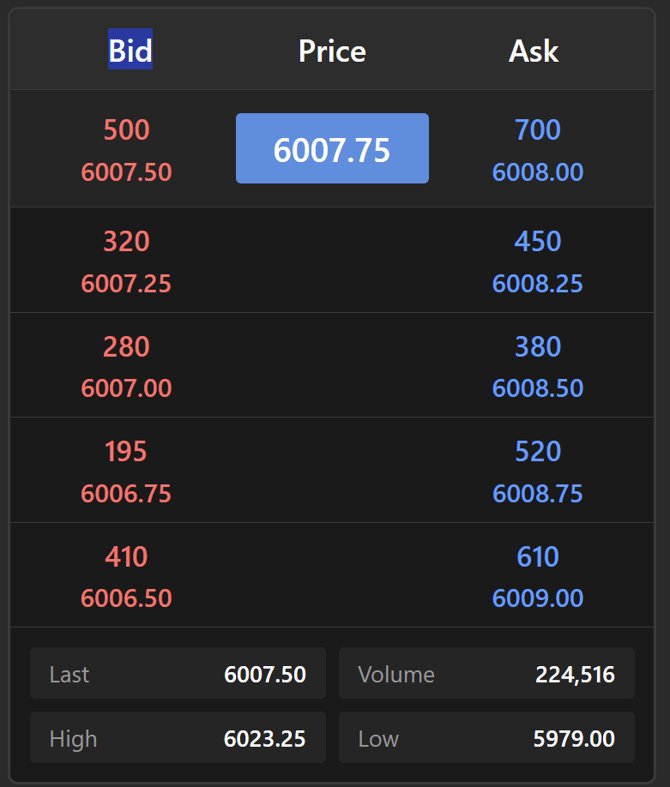
Level 2 data operates as a real-time ledger of all pending limit orders sent to the exchange. When traders place limit orders to buy or sell futures contracts at specific prices, these orders populate the order book and create the market depth display.
Core Components of Level 2 Data:
Multiple Price Levels
Instead of just showing the best bid and ask, Level 2 displays the next several price levels up and down from the current market price. In highly liquid futures like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES), you'll see orders at every tick increment.
Order Sizes at Each Price
The number of contracts waiting at each price level reveals where traders are positioning themselves. Large clusters often act as support or resistance zones.
Aggregated Order Flow
Orders from multiple participants get grouped by price point, showing total demand or supply at each level.
Real-Time Updates
Watch as orders are added, canceled, or filled in real-time, providing immediate feedback on changing market sentiment.
Example: Reading an ES Futures Order Book
Here's a simplified snapshot of the E-mini S&P 500 futures order book:
Ask Side (Sellers):
- 4801.00 — 55 contracts (Weak resistance)
- 4800.75 — 85 contracts (Building resistance)
- 4800.50 — 120 contracts (Strong resistance)
- 4800.25 — 150 contracts (Immediate resistance)
Bid Side (Buyers):
- 4800.00 — 125 contracts (Immediate support)
- 4799.75 — 95 contracts (Building support)
- 4799.50 — 75 contracts (Moderate support)
- 4799.25 — 45 contracts (Weak support)
This structure reveals potential support at 4800.00 where 125 contracts are bidding, and resistance building at 4800.50 with 120 contracts offered.
What Makes Level 2 Market Depth Unique?
Level 2 data provides several unique advantages that distinguish it from basic market data:
Predictive Market Intelligence
Unlike price charts that show what already happened, Level 2 data reveals pending intentions of market participants. Large order clusters can predict where price might stall or accelerate before the movement occurs.
Granular Liquidity Assessment
See exactly how much trading volume exists at each price level. This helps you assess whether sufficient liquidity exists to support large position entries or exits without significant slippage.
Real-Time Market Sentiment
Order flow imbalances provide immediate feedback on bullish or bearish sentiment. More aggressive buying into asks suggests bullish momentum, while heavy selling into bids indicates bearish pressure.
Enhanced Order Timing
Time your entries and exits more precisely by seeing where liquidity concentrates. Enter positions when favorable order flow develops and avoid areas where thin liquidity could cause poor fills.
Who Uses Level 2 Market Depth?
Day Traders
Short-term traders rely heavily on Level 2 data for scalping and timing entries during volatile market conditions. The real-time order flow helps them gauge momentum shifts within seconds or minutes.
Swing Traders
Medium-term traders use Level 2 to identify strong support and resistance levels that may not yet be visible on price charts. Large order clusters often become significant pivot points for multi-day moves.
Institutional Traders
Large volume traders need Level 2 data to assess liquidity before executing substantial positions. They can see if sufficient depth exists to fill large orders without moving the market significantly.
Algorithmic Trading Systems
Automated trading strategies often incorporate Level 2 data to make split-second decisions about order placement, timing, and sizing based on current market depth conditions.
What Do Market Participants Need to Know?
Order Flow Analysis Techniques
Large Cluster Identification: Look for price levels with significantly more contracts than surrounding levels. These often act as magnets for price action or barriers that require substantial volume to break through.
Thin Area Recognition: Gaps in the order book where few contracts exist can lead to rapid price acceleration if market orders push through these levels.
Imbalance Detection: Compare total bid size versus ask size near the current price. Persistent imbalances often precede directional moves.
Order Flow Shifts: Monitor how the distribution of orders changes over time. Growing bid stacks may indicate developing bullish sentiment, while expanding ask clusters suggest bearish pressure.
Common Market Depth Patterns
Support and Resistance Walls: Large concentrations of orders that act as temporary price barriers. These levels often hold multiple times before eventually breaking.
Iceberg Orders: Large orders that only show small portions to avoid revealing full size. Watch for continuous refreshing of similar-sized orders at the same price level.
Liquidity Vacuums: Areas with minimal order depth where price can move rapidly once triggered by market orders.
Platform Integration
Modern trading platforms like Optimus Flow Desktop integrate Level 2 data seamlessly with charting and order management tools. This allows traders to combine market depth analysis with technical indicators and place orders directly from the depth display.
Key Concepts for Level 2 Market Depth
Market Maker Dynamics
Market makers provide liquidity by constantly quoting bid and ask prices. Their order sizes and price levels give insight into where institutional liquidity concentrates.
Order Types and Behavior
Different order types affect the order book differently. Stop orders don't appear in Level 2 until triggered, while limit orders populate the visible depth immediately.
Spoofing Awareness
Be aware that some traders place large fake orders to manipulate perception, then cancel them before execution. While illegal, this practice still occurs and can temporarily distort Level 2 readings.
Exchange-Specific Data
Each exchange maintains its own order book. For futures, most depth comes from the primary exchange (CME for ES contracts), but some liquidity may exist on alternative venues.
Time Priority Rules
Orders at the same price level execute on a first-in, first-out basis. Understanding queue position helps assess likelihood of fills at specific price levels.
Hidden Liquidity
Level 2 doesn't show all available liquidity. Dark pools, iceberg orders, and other hidden order types can create surprise liquidity that doesn't appear in the visible depth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 market data?
Level 1 shows only the best bid and ask prices with sizes, while Level 2 displays multiple price levels above and below the current market with order sizes at each level. Level 2 provides much deeper insight into market structure and pending supply/demand.
How much does Level 2 data cost for futures trading?
Most professional futures platforms include Level 2 data with standard market data packages. At Optimus Futures, Level 2 depth is available through our trading platforms with competitive data fees and low commission pricing.
Can Level 2 data predict price direction?
Level 2 shows pending orders but cannot guarantee price direction. Large order imbalances provide clues about potential moves, but orders can be canceled instantly and hidden liquidity may exist. Use Level 2 as one component of a comprehensive trading strategy.
What futures contracts have the best Level 2 data?
Highly liquid contracts like E-mini S&P 500 (ES), crude oil (CL), and treasury futures provide the richest Level 2 data with tight spreads and substantial depth. Less liquid markets may show sparse order books with wide gaps between price levels.
How do I avoid being misled by fake orders in Level 2?
Focus on confirmed order flow rather than static order sizes. Watch for orders that consistently cancel before execution and verify Level 2 signals with price action and volume patterns. Combine multiple analysis methods rather than relying solely on market depth.
Should beginners use Level 2 data for futures trading?
Start with understanding futures basics and risk management fundamentals before adding Level 2 complexity. Once comfortable with basic trading concepts, Level 2 can enhance decision-making and order timing.
How does leverage affect Level 2 trading decisions?
High futures leverage makes precise entry and exit timing crucial. Level 2 helps identify optimal entry points and liquidity for position sizing, but always maintain proper risk management regardless of market depth readings.
Can I trade successfully without Level 2 data?
Many successful traders rely primarily on price charts and Level 1 data. Level 2 provides additional insight but isn't mandatory for profitable trading. Focus on developing sound trading principles and risk management before adding advanced tools.
What's the best way to learn Level 2 interpretation?
Practice with simulated trading to observe order flow without risk. Study Level 2 behavior around key support/resistance levels and during news events. Start with highly liquid futures contracts where patterns are clearest.
How does market volatility affect Level 2 reliability?
High volatility increases order cancellations and rapid depth changes, making Level 2 more challenging to interpret. During volatile periods, focus on confirmed order flow rather than static depth readings and maintain wider stop losses to account for increased uncertainty.
Next Steps in Your Futures Education
Master the Fundamentals:
- ✅ Level 2 market depth overview (covered in this article)
- Contract mechanics → What are Futures Contracts?
- Risk management → Understanding Futures Risk
Apply Your Knowledge:
- Market selection → Stock Index Futures
- Position sizing → Position Sizing Principles
- Order execution → Understanding Market Orders
Develop Trading Skills:
- Day Trading Fundamentals for short-term strategies
- Swing Trading Fundamentals for multi-day approaches
- Essential Stop Loss Strategies for capital protection
Risk Disclaimer
The content of this guide is the opinion of Optimus Futures.
Futures and options trading involves substantial risk and is not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. Examples provided are for illustrative and educational purposes only and should not be construed as specific trading advice or recommendations.
Trading on margin and with leverage carries a high level of risk, as it can amplify both gains and losses.
The placement of contingent orders such as "stop-loss" or "stop-limit" orders will not necessarily limit your losses to the intended amounts, since market conditions may make it impossible to execute such orders. Risk management techniques discussed (such as stops, stop-limits, or bracket orders) cannot eliminate risk.
You should only trade with risk capital—that is, money you can afford to lose without affecting your lifestyle or financial security. There are no “proven” methods or guaranteed systems for making money in futures trading. It is a challenging process that requires ongoing learning, discipline, and adapting to changing market conditions. Traders must carefully consider their financial condition, risk tolerance, and trading objectives before engaging in futures or leveraged markets. It is important to note that most traders do lose money trading futures.
